Mechanosensation and Mechanosensitive Ion Channels
- Structure and Dynamics of Mechanosensitive Ion Channels
We study mechanosensitive ion channels in order to understand the fundamental biophysical property of mechanosensation, a universal mechanism for ion channel regulation. Mechanosensitive channels in bacteria protect the cell against extreme osmotic conditions acting as pressure safety valves and in higher organisms are involved in hearing, touch and cardiovascular architecture. We believe key to their function is the lipid, which transmits membrane tension from and to the channels and we therefore aim elucidating its role at a molecular level.


- Characterisation of Novel Mechanosensitive Ion Channels
We recently characterised two eukaryotic mechanosensitive channels, named MscA and MscB from the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans
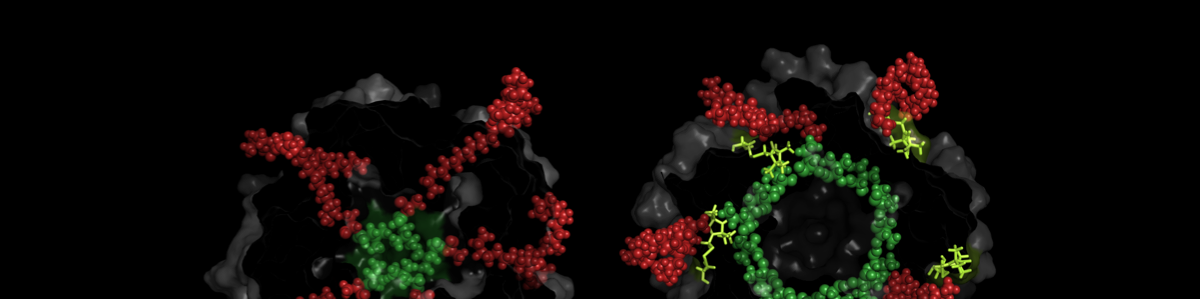
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Spectroscopy on Membrane Proteins
- PELDOR (or DEER) Spectroscopy
Cysteines are engineered to the sites of interest by site directed mutagenesis. Spin labels, such as MTSSL are introduced, specifically react with the cysteines and modify them. Multimeric proteins carry more than a single spin label per macromolecule and pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), PELDOR (also known as DEER) spectroscopy is facilitated to give rise to spin-to-spin distances within the complex and provide high quality structural information in native/lipid environment.


Pliotas et al., PNAS, 2012 ; Ward et al., Biophys J, 2014; Pliotas, Methods Enzymol, 2017 ; Michou et al., ACS Synth Biol, 2019 ; Kapsalis et al., Nat Comms, 2019 ; Kapsalis et al., Biophys J, 2020 ; Hartley et al., RSC Electron Paramag Reson, 2020 ; Wang, Lane et al., Structure, 2022; Lane, Ma, Yan et al., Structure, 2024
- ESEEM Spectroscopy
Alongside PELDOR, Electron Spin Echo Envelope Modulation (ESEEM) spectroscopy is used to gain insights into Deuterium (solvent) accessibility of key residues, crucial for membrane protein regulation. For ESEEM we use the same frozen spin labelled protein samples (PELDOR) to complement PELDOR distance measurements and develop accurate and reliable gating models for ion channels and transporters.